It’s been exactly one year since I started my journey as a NumPy Fellow, and looking back, it has honestly been the best job I’ve ever had. My main goal for 2025 was to push the boundaries of static typing within the Scientific Python ecosystem. I’m happy to report that we didn’t just push the boundaries; we reshaped them.
Here is a high-level look at what we achieved, from making numpy fully type-checked to bridging the gap between scientific computing and the wider Python typing community.
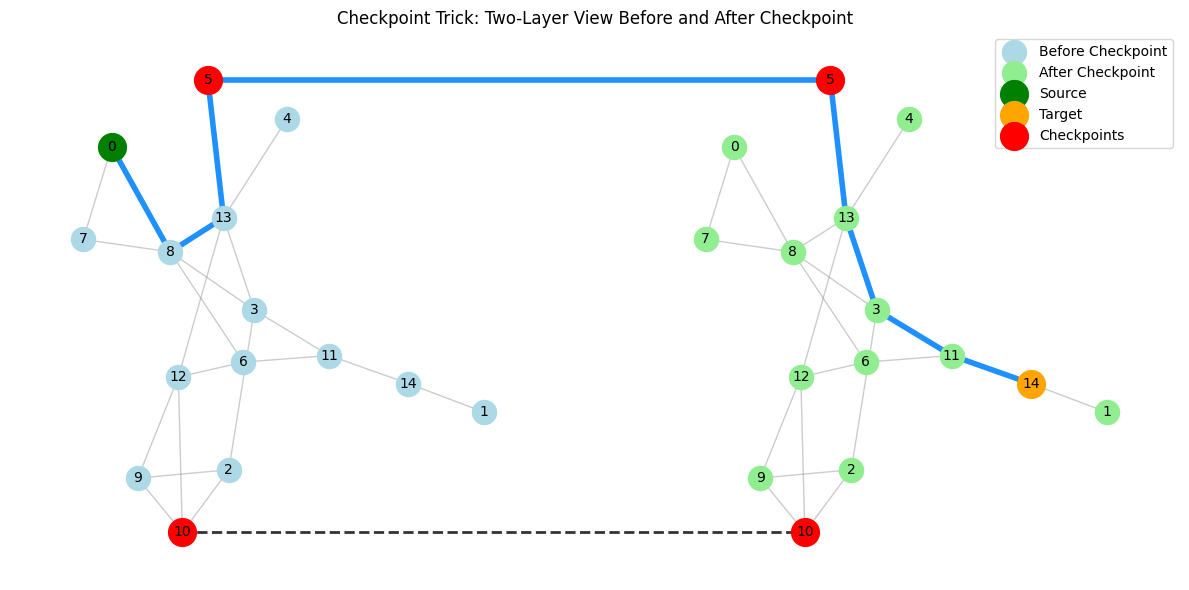 Many real-world shortest path problems include constraints that classic algorithms don’t directly handle. NetworkX provides robust, optimized implementations of algorithms like Dijkstra’s, Bellman-Ford, and A*. But what if your problem doesn’t fit the classic shortest path formulation?
Read more...
Many real-world shortest path problems include constraints that classic algorithms don’t directly handle. NetworkX provides robust, optimized implementations of algorithms like Dijkstra’s, Bellman-Ford, and A*. But what if your problem doesn’t fit the classic shortest path formulation?
Read more...
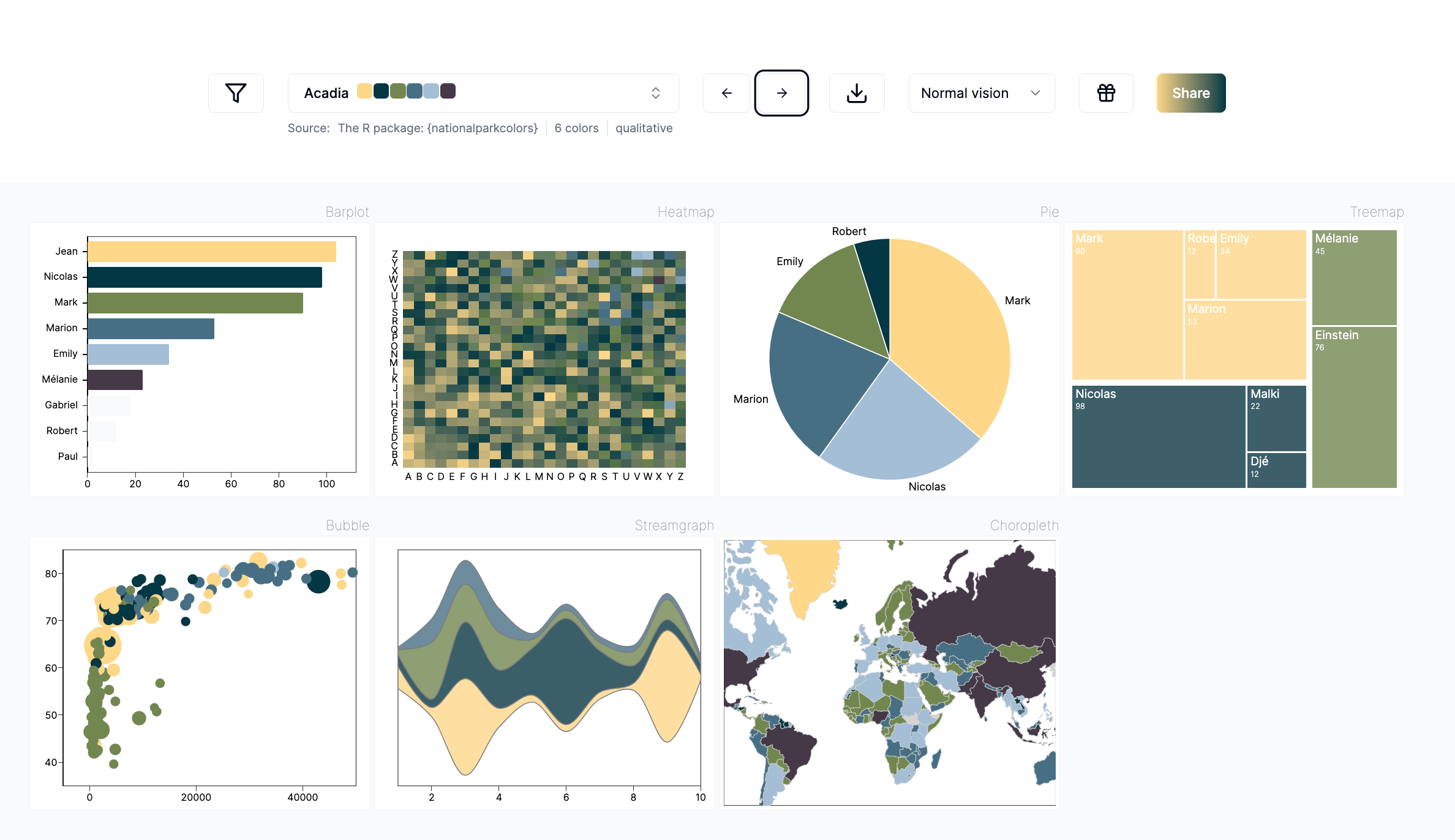 PyPalettes is a new Python library designed to simplify the use of color palettes in Python charts.
Read more...
PyPalettes is a new Python library designed to simplify the use of color palettes in Python charts.
Read more...
The NumPy team is excited to announce the appointment of Joren Hammudoglu (@jorenham) as the second NumPy Developer in Residence. For the second time, the project is in a position to use its project funds to pay for a full year of maintainer time through the NumPy Fellowship Program.
Joren has been the driving force behind the improvements in NumPy’s support for static typing since he started contributing in mid-2024. He has authored a lot of the improvements — from the annotations themselves to CI support and working towards fundamental design improvements like ndarray shape typing — and helps guide and integrate the work of other NumPy contributors in this area, and engages with upstream projects like MyPy and Pyright and the typing standards/PEP process to help move static typing support for the ecosystem as a whole forward. He also contributes widely to static typing support in the ecosystem, as the author of scipy-stubs, numtype and more.
 The 2024 Scientific Python Developer summit was held 3–5 June in Seattle. Here’s a summary of what we did.
Read more...
The 2024 Scientific Python Developer summit was held 3–5 June in Seattle. Here’s a summary of what we did.
Read more...
TL;DR: If you have GPU code in your project, setup a GitHub hosted GPU runner today. It is fairly quick to do and will free you from having to run tests manually.
Read more...